Automatic app versioning for Android - the easy way

Android application versioning is one of those things during project development that you set up once at the beginning and forget about it. But as with everything in project configuration, I think it’s important for it to be robust. To be easy to understand and easy to change.
So, let me show you how to achieve automatic app versioning the easy way. This method has been working for me on many Android projects.
I hope you’ll find it useful too.
The gist of this is that you’ll use git commands executed in build.gradle to set the versionCode and versionName. To use this method, you need to have `git` installed in your system and initialized git repository in your project.
First, let’s see the commands you’ll use for each value.
Jump to a section
Version code:
For the versionCode, which is supposed to be an Integer value, we’ll use a number of commits on the current branch. It’s as simple as it can get, more commits, a higher version. But beware that it works great when you’re using a single branch like main to produce release builds. Otherwise, you might want to go in an entirely different direction with the versioning system.
To get the number of commits, we can use this command:
git rev-list --count HEAD
Version name:
For the versionName, we’ll use tagging functionality and describe command. First, you’ll need to create a tag. You can do so using this command git tag -a 1.0 -m "1.0". We’re using what is called an annotated tag. There are also lightweight tags, but the difference is that annotated ones also contain a message, just like a commit. We’re using annotated because they have that additional info, which can be useful. Also, some commands (like describe below) uses only annotated by default and ignores the lightweight ones, which also might be useful when you can still use the lightweight for some other purpose in your project.
To get the version name, we’ll use a describe command.
git describe
This command behaves interestingly. If your last commit has a tag, it’ll output only the name of the tag. But if there are some untagged commits on top of the last tag, it’ll output the name of the tag and some additional information. This is what it can look like 1.0-3-g24cd732.
Let’s decode it, 1.0 is your last tag on the branch, 3 is the number of untagged commits on top of the last tagged commit, g24cd732 is a hash code of the last commit (symbol g is hard-coded, and can be ignored).
Implementation:
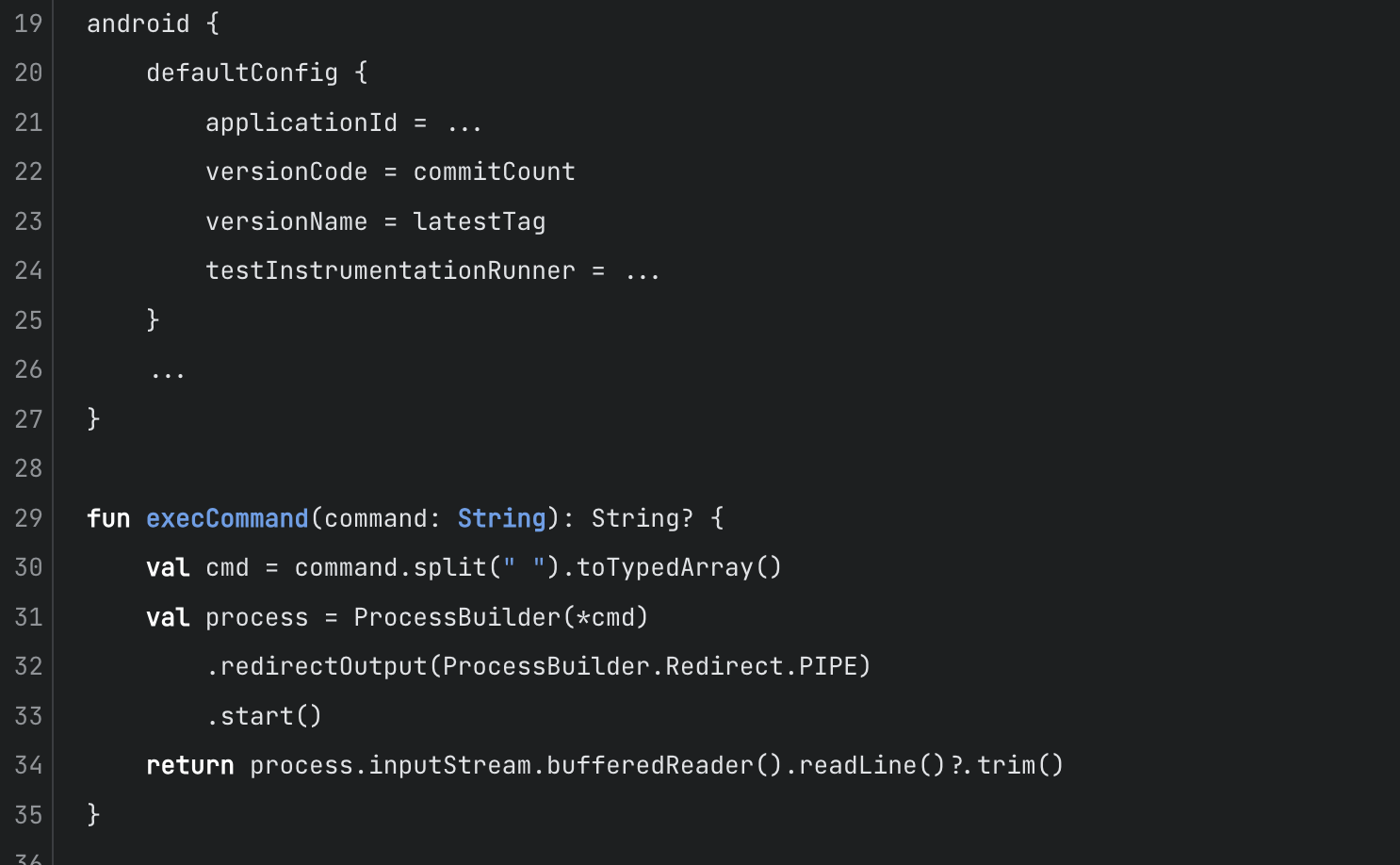
The first step is the ability to call shell commands from gradle files. Here’s how it looks like in gradle kotlin script:
fun execCommand(command: String): String? {
val cmd = command.split(" ").toTypedArray()
val process = ProcessBuilder(*cmd)
.redirectOutput(ProcessBuilder.Redirect.PIPE)
.start()
return process.inputStream.bufferedReader().readLine()?.trim()
}
The next step is to use this method to get the values we want in the app/build.gradle.kts
plugins {
...
}
val commitCount by project.extra {
execCommand("git rev-list --count HEAD")?.toInt()
?: throw GradleException("Unable to get number of commits. Make sure git is initialized.")
}
val latestTag by project.extra {
execCommand("git describe")
?: throw GradleException(
"Unable to get version name using git describe.\n" +
"Make sure you have at least one annotated tag and git is initialized.\n" +
"You can create an annotated tag with: git tag -a 1.0 -m \"1.0\""
)
}
android {
defaultConfig {
applicationId = ...
versionCode = commitCount
versionName = latestTag
testInstrumentationRunner = ...
}
...
}
fun execCommand(command:String): String? {
val cmd = command.split(" ").toTypedArray()
val process = ProcessBuilder(*cmd)
.redirectOutput(ProcessBuilder.Redirect.PIPE)
.start()
return process.inputStream.bufferedReader().readLine()?.trim()
}
And that’s it, automatic app versioning, the easy way. 🎉
Using describe command for versionName gives us useful additional info, for example when we’re distributing an app version to testers before the release.
It shows exactly what commit was used to generate each apk. The version name will be available in the crashlytics, or be attached to bug tickets. You can utilize it and jump straight into the commit that contains reported bugs or has produced exceptions.
But it also might have some negative consequences. Imagine releasing production app with this version name 1.0-3-g24cd732. It’s not readable and might even look suspicious to non-technical users. This elongated versionName should be used only for dev and test builds, you shouldn't create release builds with it, but it might be easy to do so by accident.
We can add a task in the gradle to automatically check every time we’re compiling a release build if the versionName has the correct value. Here’s how it can be done in app/build.gradle.kts file.
plugins {
...
}
android {
defaultConfig {
...
}
...
}
plugins {
...
}
android {
defaultConfig {
...
}
...
}
tasks.whenTaskAdded {
if (name.contains("assemble") &&
name.contains("Release")
) {
dependsOn("checkReleaseVersion")
}
}
tasks.register("checkReleaseVersion") {
val versionName = android.defaultConfig.versionName
if (versionName?.matches("\\d+(\\.\\d+)+".toRegex()) == false) {
throw GradleException(
"Version name for release builds can only be numeric (like 1.0), but was $versionName\n" +
"Please use git tag to set version name on the current commit and try again\n" +
"For example: git tag -a 1.0 -m 'tag message'"
)
}
}
This task checks with regex when compiling release builds (with any flavors) if the versionName contains only digits and dots, like 1.0. If you’ll try to create release builds on an untagged commit (with versionName like 1.0-3-g24cd732), the build process will fail.
Thanks to this approach, we’re also ensuring that only tagged commits were used to create release builds.
Clean up
If you’re using convention plugins or buildSrc folder, you can extract that logic from gradle files to one of those directories. I like to make a single file with name AppVersioning.kt, and put all the logic in there:
/**
* Get the version code from the number of commits.
* Command: git rev-list --count HEAD
*/
fun getVersionCode(): Int {
return execCommand("git rev-list --count HEAD")?.toInt()
?: throw GradleException("Unable to get version code. Make sure git is initialized.")
}
/**
* Get the version name from the latest annotated tag.
* Command: git describe
*/
fun getVersionName(): String {
return execCommand("git describe")
?: throw GradleException(
"Unable to get version name.\n" +
"Make sure you have at least one annotated tag and git is initialized.\n" +
"You can create an annotated tag with: git tag -a 1.0 -m \"1.0\""
)
}
private fun execCommand(command: String): String? {
val cmd = command.split(" ").toTypedArray()
val process = ProcessBuilder(*cmd)
.redirectOutput(ProcessBuilder.Redirect.PIPE)
.start()
return process.inputStream.bufferedReader().readLine()?.trim()
}
➡️ Tip: If you put the AppVersioning.kt file in the root kotlin folder instead of a package, you don’t have to add any imports when using getVersionCode() and getVersionName() in the build.gradle.kts.
This is how the path might look like with the convention plugin:
MyApplication/build-logic/convention/src/main/kotlin/AppVersioning.kt
Bitrise CI
If you're using Bitrise CI/CD, remember to change Fetch tags option in Git Clone Repository step. Otherwise, versioning won't be working in workflows.
Workflow > Git Clone Repository > Clone Config > Fetch tags > change from "no" to "yes"
Git flow
As for the git flows, you have to be careful if this versioning method is compatible with what you’re doing in your project. I always like to use something simple and then change the flow if the project actually needs it. This is an approach I’d recommend if you’re not sure:
Use 3 types of branches:
main- contains released or ready for release code. The last commit must always be tagged with the latest version.develop- contains changes ready to be tested. Accumulate commits until you’re ready for a release. When you want to release a new version, given it's already been tested. Tag it ondevelopbranch, then rebase the changes tomain. Thanks to thismainwill have the same history and the same tagged commits asdevelop.- Feature branches, like
feature/my_feature. Work on each feature on separate branches, when they're complete, squash and merge them todevelop.
----
Thank you for reading!
You can find a working playground example on my Github repo: HERE
And to learn about the software development process in the Untitled Kingdom, check out this page.
----
The original version of this article appeared on easycontext.io on the 4th of August
